Applicant
Prof. Dr. Helena Liebelt
Director Institute Future Technologies
Program Director MA High Performance and Quantum Computing
Deggendorf Institute of Technology (DIT)
Project Overview
Hydrogen plays a central role in the energy and heat transition; however, the production cost of green hydrogen remains high. Currently, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is already being applied to reduce these costs by optimizing production processes, including electrolyzer scheduling, operational flexibility, and the utilization of byproducts such as waste heat. Such AI-based optimization approaches have demonstrated efficiency gains of up to 35% and cost reductions in the range of 30–50% [1].
Quantum computing, as an emerging technology, offers a fundamentally new perspective on optimization and AI-driven decision-making. This project focuses on the development and validation of a quantum-AI-based optimization model for green hydrogen production, storage, and transport. The model explicitly considers additional system components and coupling effects, including thermal energy usage and battery storage, enabling a holistic optimization of integrated energy systems (see Fig. 1).
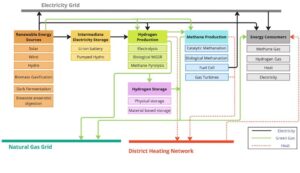
Figure 1
The proposed quantum AI model will build on established quantum-mathematical optimization methods, including Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization (QUBO), Higher-Order Unconstrained Binary Optimization (HUBO), and the Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA). The objective is to assess their applicability, performance, and added value compared to classical AI-based optimization approaches in real-world hydrogen energy systems.
References
[1] Bhuiyan, Sharif Md Yousuf, et al. “AI-Driven Optimization in Renewable Hydrogen Production: A Review.” American Journal of Interdisciplinary Studies 6.1 (2025): 76-94.

